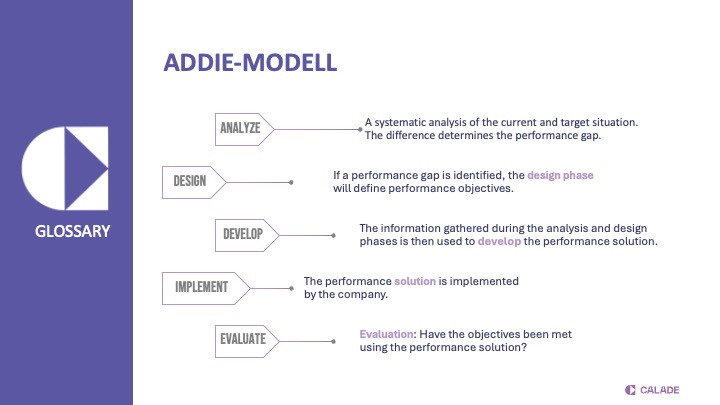
The ADDIE model is a five-phase framework from instructional design—Analysis, Design, Development, Implementation, and Evaluation. In change contexts, it structures the work from framing problems through designing interventions to robust outcome evaluation—for organizational development, team development, and transformations.
Origin and Purpose
Developed in the 1970s at Florida State University for the U.S. military, ADDIE was created to design training systematically and close performance gaps. The same logic applies to change: analyze carefully, design for outcomes, develop lean, implement with discipline, and evaluate rigorously—tool-agnostic and adaptable.
Core Phases in a Change Context
- Analysis – Assess current/target states, identify root causes, stakeholders, performance gaps, and risks.
- Design – Define target state, principles, intervention architecture, governance, roadmap, and co-design with those affected.
- Development – Create artefacts: processes, training/coaching materials, communication packages, KPIs, dashboards; pilot for quality assurance.
- Implementation – Wave-based rollout, activate sponsors and champions, on-the-job coaching, active impediment removal.
- Evaluation – Measure outcomes, identify lessons, reinforce successful practices, and anchor changes culturally.
Application and Best Practices
- Do not shortcut analysis – otherwise only symptoms are treated.
- Design for outcomes – link interventions to measurable behavior and performance changes.
- Develop modularly – pilot and prototype to enable early learning.
- Implement in waves – visible sponsorship and active impediment clearing are key.
- Treat evaluation as continuous – set baselines early, measure during, sustain after.
Practice Examples
Insurance digitalization: ADDIE helped streamline processes, combine training with clear decision paths, and learn iteratively through pilots. Result: faster cycle times, higher customer satisfaction.
Post-merger integration: Governance structures were redefined, a new operating model designed, and employees engaged via shadow boards. Success factors: visible sponsorship and systematic evaluation.
Frequent Pitfalls and Remedies
- Linearity trap: Using ADDIE sequentially delays learning. → Build in iterations and feedback loops.
- Training fixation: Over-reliance on training ignores structural/system levers. → Address processes, incentives, and systems.
- Symptom treatment: Skipping root-cause analysis leads to expensive quick fixes. → Validate hypotheses with data.
- Vanity metrics: Focusing on outputs, not outcomes. → Define clear leading/lagging indicators.
- Sponsor drift: Sponsors fade after kick-off. → Sponsor roadmap, visible rituals, escalation paths.
- Over-engineering: Perfect artefacts, late learning. → Prototype early, adopt agile elements.
- Broadcast-only communication: Information instead of involvement. → Enable co-design and feedback loops.
Measurement and Evaluation
- Leading: Adoption and usage rates, first-time-right, cycle times.
- Lagging: Quality, cost, delivery, customer outcomes.
- Experience: Pulse surveys, observations, retrospectives.
- Governance: Cadence of reviews, escalation paths, lessons learned.
Relation to Alternatives
- ADKAR: Focus on individual adoption.
- Kotter: Leadership and momentum.
- ACMP Standard: End-to-end change management framework.
- Lewin: Classical three-phase model.
- SAM: Iterative alternative with prototyping focus.
CALADE Perspective
CALADE applies ADDIE as a structuring spine—pragmatically, context-aware, and combined with complementary models. In advisory projects, ADDIE provides clarity and order while allowing flexibility, reinforced with elements from ADKAR, Kotter, or ACMP. This approach ensures measurable outcomes, short learning cycles, and systematic impediment removal.
Cross-references to related glossary entries
- ACMP Standard Methodology
- ADKAR
- Kotter’s 8-Step Model
- Commitment Curve
- Lewin’s Three-Phase Model
- Timeboxing
- Impediment
- Built-in Quality (SAFe)
← back to list